Unusual Colour Film Sensitivities
There have been a number colour films made where the colour image produced on the film does not follow the usual correlation of the colour of the exposing light to the dyes produced. For the fairly obvious reason that the whole point of photographing in colour is to get correct colour reproduction, they were usually colour print or duplicating films where the correlation did not affect the final result.
The order of the layers was changed so that the magenta layer was on top because it is the sharpest layer. 'Eastman' Color Print film has the magenta layer on top although it has the normal relationship of sensitivity/dye of blue/yellow, green/magenta and red/cyan. Most early emulsions when colour sensitised were still sensitive to blue as well as red or green. If the normal order of layers was maintained a filter was need to stop the blue light reaching the other two layers. This is usually colloidal silver, very fine particles of silver which absorb blue light. The layer is removed during the normal bleach process to remove the silver image formed during developing.
All camera films have the yellow filter layer with the exception of 'Kodak' Infrared Ektachrome where one layer, which produced cyan dye, was sensitive to infrared . Infrared Ektachrome was devised during the Vietnam War and its purpose was for aerial photography to detect camouflage. Military vehicles, guns, buildings and so on often are camouflaged by using nets with brown and green fabrics woven into them. From the air this cannot be distinguished from normal trees and foliage. Because green leaves contain chlorophyll a substance that reflects infrared, leaves appear magenta using the IR Ektachrome stock whilst fabric that does not reflect IR will appear their normal green or brown colour. Subsequent to the war the film was used by directors who required strange or ‘psychedelic ’ colours in their film. It was also used to detect various diseases in plants and trees where such diseases caused loss or change to the chlorophyllin leaves and foliage. The actual colours achieved would depend on filters used as well as the exposure.


Some of the films that had different sensitivities were 'Kodak' Colour Internegative 5245, Gasparcolor, and 'DuPont' Type 275 Colour print .
'Kodak' Colour Internegative 5245 had a blue sensitive layer that produced magenta dye; a green sensitive layer that produced cyan dye and a red sensitive layer that produced yellow dye.
Please click image to see a larger image
Another film where the colour of the dye produced did not have the normal relationship to the colour sensitivity of the layer was Gasparcolor. This was a reversal colour print stock that was used for making colour prints from separation positives . It used the process called dye destruction .

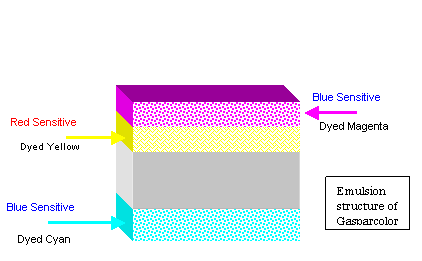
The film was designed to be printed from separation positives so that the relationship of the sensitivity to the colour of the dye produced did not matter. You just had to remember to make the exposure of the green separation with blue light; the blue separation with red light and the red separation with blue light again. As can be seen from the diagram the cyan layer was on the opposite side to the magenta and yellow layers. The red exposure was made from the other side of the film; the magenta layer, which was also blue sensitive, was protected from exposure by the yellow dye layer underneath the magenta layer. See separate article on Gasparcolor detailing the film and process.
DuPont type 275 had a top layer that was blue sensitive and produced magenta dye, a second layer sensitive to red producing a cyan dye and a bottom layer that gave yellow dye.
As with all films that have non-standard sensitivity/dye relationships this film has to be printed from separation negatives.The green separation would be exposed using a blue filter so that the blue sensitive later is exposed producing magenta dye. The blue separation would be exposed using a green filter and the red separation using a red filter.


